 Last updated: August 23rd, 2024
Last updated: August 23rd, 2024
Keeping You Cozy: A Comprehensive Guide to Central Heating Systems
Imagine stepping into a toasty home on a chilly winter day. The comfort of central heating is a modern marvel, silently warming your entire house with efficient circulation. But what exactly is a central heating system, and how can you keep it functioning optimally throughout the seasons? This comprehensive guide delves into central heating, exploring its components, common problems, solutions, and maintenance tips.
Understanding Your Central Heating System: The Basics
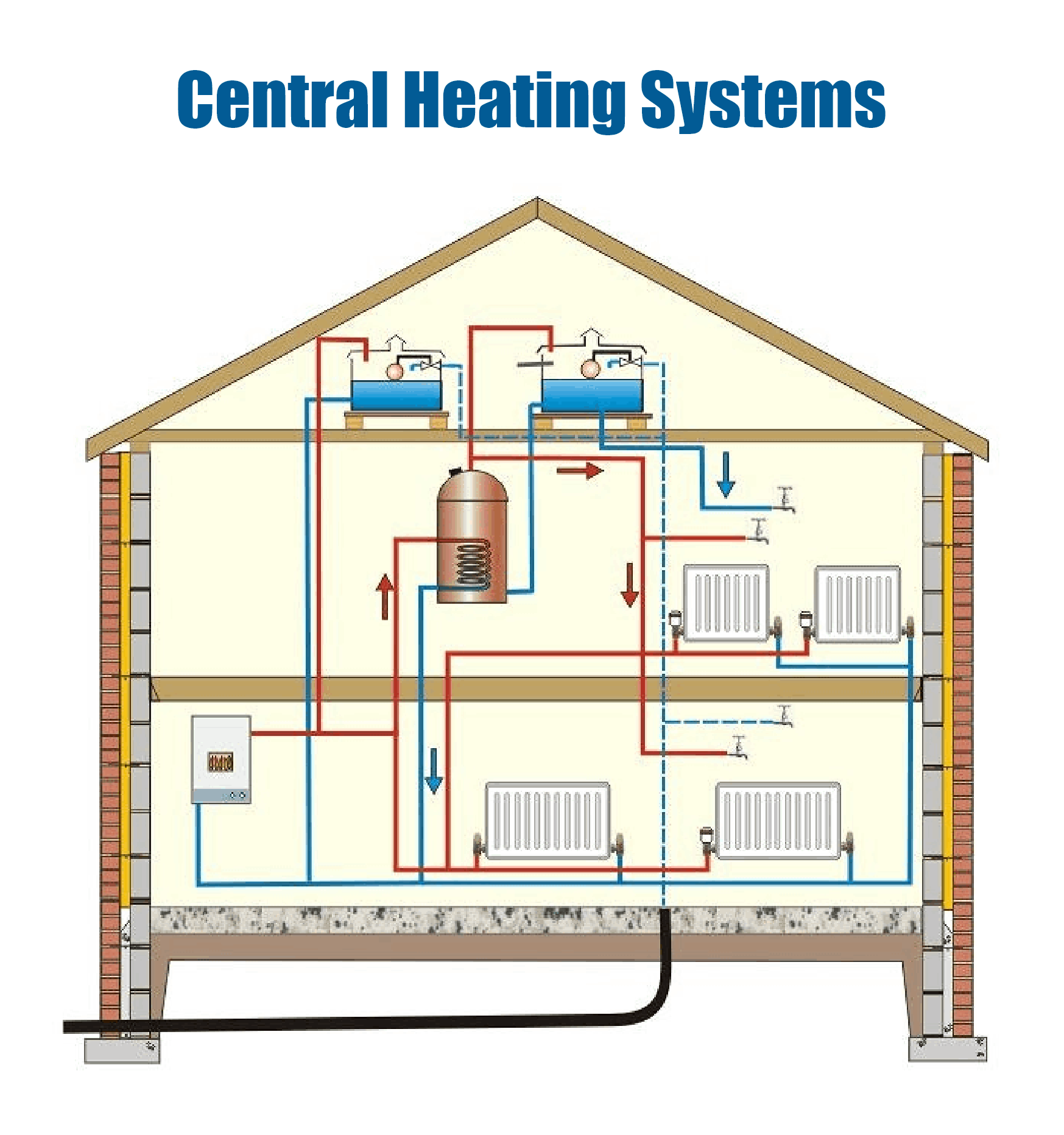
A central heating system acts as the heart of your home’s warmth. It consists of three main components working in tandem:
- Heat Source: This is where the heat originates. Common options include boilers (gas, oil, or electric) and heat pumps.
- Distribution System: This network of pipes or ducts carries the heated water or air throughout your house.
- Heat Emitters: These are the devices that release heat into your living space. Radiators and forced-air vents are the most common types.
4 Common Central Heating Systems
Now that we understand the core components, let’s explore the different types of central heating systems available:
- Boiler Systems
- Function: Boilers burn fuel (gas, oil, or propane) to heat water. This hot water then circulates through pipes to radiators or radiant floor heating systems, radiating heat into your home.
- Pros: Highly efficient, especially with gas boilers. Reliable heat source, particularly in colder climates.
- Cons: Requires annual maintenance. Oil boilers can be more expensive to operate.
- Forced-Air Systems
- Function: A furnace burns fuel (gas, oil, or electric) to heat air. This hot air is then distributed through a network of ducts to vents throughout your home.
- Pros: Relatively affordable installation. Heats your home quickly. It can be integrated with air conditioning systems for year-round climate control.
- Cons: It can be less energy-efficient than boiler systems. Forced air can cause dust circulation and dryness.
- Heat Pumps
- Function: These innovative systems act like a two-way air conditioner. In heating mode, they extract heat from the outside air (even in colder climates) and transfer it to your home through a forced-air system. In cooling mode, they reverse the process, removing heat from your home and releasing it outdoors.
- Pros: It is highly energy-efficient, especially in moderate climates. It can provide both heating and cooling. It is also environmentally friendly.
- Cons: Installation costs can be higher than those of traditional systems. Efficiency can decrease in frigid climates.
- Radiant Heating Systems
- Function: Radiant heating systems use radiant heat, which warms objects and surfaces directly rather than heating the air. This can be achieved through hydronic radiant floor heating (hot water circulated through pipes under the floor) or electric radiant panels installed in walls or ceilings.
- Pros: Provides a very comfortable and even heat distribution without contributing to dust circulation.
- Cons: Installation costs can be higher than those of traditional systems. It may only be suitable for some types of flooring.
However, even the most robust systems can encounter issues, leaving you shivering and frustrated. Let’s go to the section below and learn about significant central heating issues and their DIY fixes.
Top Central Heating Problems & Troubleshooting Tips
Before attempting any repairs yourself, always ensure safety is your top priority. Call a qualified HVAC technician if you’re uncomfortable or unsure about any step.
1. No Heat: The most obvious sign is that your home isn’t getting warm, even when the thermostat is set to “heat.”
DIY:
- Check the Thermostat: Ensure it’s set to “heat” and at a desired temperature. Check for any low battery warnings on programmable thermostats.
- Inspect the Pilot Light (Gas Systems): If extinguished, relight it according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Safety Note: Only attempt this if you’re comfortable and follow all safety precautions outlined in the manual.
- Check the Fuel Supply: Ensure enough gas or oil in the tank and no electrical issues are affecting the system.
2. Uneven Heating: Some rooms feel warm while others remain chilly, indicating potential distribution issues.
DIY:
- Bleed the Radiators (Hot Water Systems): Air trapped in radiators can cause cold spots. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for bleeding the system.
- Check Airflow (Forced-Air Systems): Blocked vents or clogged filters can restrict airflow. Clean or replace air filters regularly. Ensure vents are not blocked by furniture or rugs.
- Zone Control Issues (if applicable): Zone control systems allow different temperature settings in various areas. Ensure the zones are functioning properly and programmed correctly.
3. Strange Noises: Your heating system shouldn’t sound like a horror movie soundtrack. Banging, rattling, or gurgling noises can point to internal problems.
DIY:
- Gurgling or Knocking (Hot Water Systems): This can indicate air in the pipes. Refer to the bleeding instructions above.
- Banging or Clanking: Loose pipes or malfunctioning internal components might be the culprit. Call a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair.
4. Leaks: Water leaks around radiators or pipes are a red flag and require immediate attention.
DIY:
- Small Leaks: Tighten loose fittings or replace worn gaskets. For larger leaks, call a professional immediately. Safety Note: Do not attempt to fix a major leak yourself. Shut off the system and call a qualified technician to address the issue.
When to Call in the Professionals: Signs You Need Help
While some problems might be manageable with a little DIY effort, there are situations where professional help is essential:
- No Success with Troubleshooting: If you’ve tried the basic fixes and your heating system is still malfunctioning, call a technician for a proper diagnosis and repair.
- Safety Concerns: If you suspect a gas leak or carbon monoxide issue, shut off the system immediately and evacuate the house. If necessary, call a qualified technician and emergency services.
- Major Component Failure: If a major component, such as the boiler or furnace, seems to be failing, professional repair or replacement is likely necessary.
When to Consider Replacing Your Central Heating System
While repairs may extend the life of your system by a few months/years, some signs indicate a replacement might be necessary:
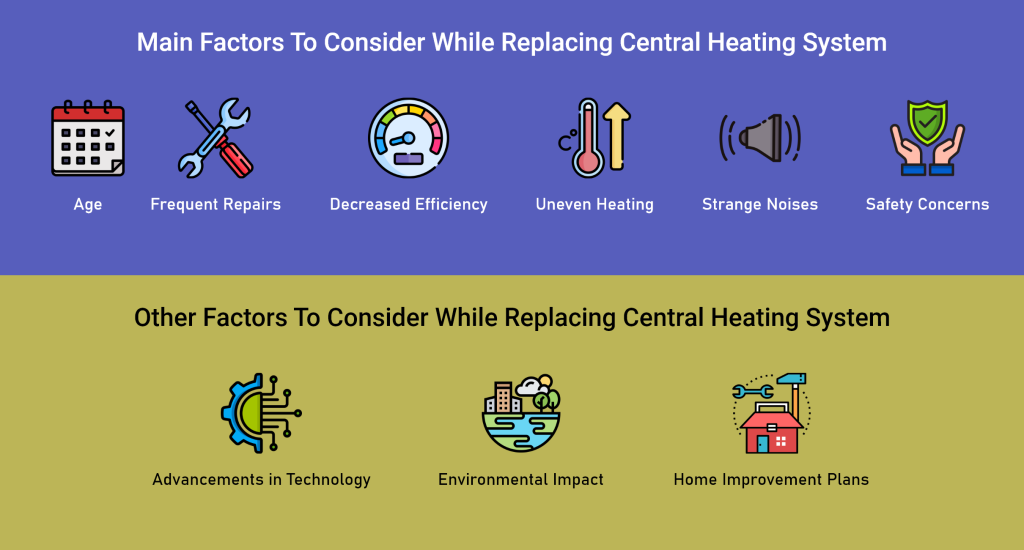
- Age: Like all machines, central heating systems have a finite lifespan. They can last anywhere from 10 to 15 years, depending on various factors.
- Frequent Repairs: Constantly needing repairs can drain your finances and time. If your system requires frequent attention, a newer, more efficient model might be a more cost-effective solution in the long run.
- Decreased Efficiency: Older systems are less efficient at converting fuel into heat, leading to higher energy bills. Replacing your system with a newer, high-efficiency model can significantly reduce heating costs.
- Uneven Heating: Homes with uneven hot and cold zones could have failing components or an inefficient distribution system. A new system might offer more consistent and comfortable heating throughout the house.
- Strange Noises: Your heating system shouldn’t sound like a haunted house. Banging, rattling, or grinding noises can indicate internal wear and tear, potentially leading to significant breakdowns.
- Safety Concerns: If you suspect a gas leak or carbon monoxide issue, shut off the system immediately and call a qualified technician. In some cases, a complete system replacement might be necessary to ensure the safety of your home.
Other Factors to Consider When Replacing Your Heating System
While age is a significant factor, other aspects can influence your decision to replace your central heating system:
- Advancements in Technology: Newer heating systems are more efficient and quieter and often come with advanced features like smart thermostats for improved control and energy savings.
- Environmental Impact: High-efficiency systems save money and reduce your carbon footprint. Consider environmentally friendly options like geothermal heat pumps.
- Home Improvement Plans: If you’re planning a major renovation project, replacing your heating system during this time might be more convenient and cost-effective due to easier access and potential integration with other upgrades.
5 Questions You Must Ask The Experts
Before making a final decision, consulting a qualified HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) technician is crucial. They can assess your existing system, evaluate your needs and budget, and recommend the most suitable replacement option. Here are some questions to ask your technician:
- Is a repair possible, or is a replacement necessary?
- What are the different types of heating systems available for my home?
- What factors should I consider when choosing a new system?
- What is the estimated cost of replacing my heating system?
- What financing options are available (if applicable)?
By getting professional advice, you can make an informed decision that ensures comfort, efficiency, and long-term cost savings for your home.
Additional Considerations: Extending the Life of Your System
Even if your heating system isn’t quite ready for replacement, there are steps you can take to prolong its lifespan and optimize its performance:

- Regular Maintenance: Schedule annual servicing with a qualified technician to ensure proper operation, identify potential problems early on, and maintain efficiency.
- Change Air Filters Regularly: Dirty air filters restrict airflow and reduce efficiency. Replace air filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Upgrade Your Thermostat: Consider installing a smart thermostat for programmable heating and remote control, which will maximize efficiency and comfort.
- Clean Vents and Registers: Regularly clean vents and registers to prevent dust buildup from obstructing airflow.
- Protect With A Home Warranty: Unexpected repairs can be a financial burden. Home warranties offer a safety net for essential home appliances and systems, including central heating.
Understanding Home Warranties: A Safety Net for Your Central Heating Systems
A home warranty is a service contract between you and a home warranty company. You pay an annual premium for coverage against the breakdown of major appliances and systems, including your central heating system.
Coverage For Central Heating
While specific coverage details can vary by company and plan, home warranties typically cover repairs or replacements for essential components of your central heating system, including:
- Furnaces: Repairs for electrical components, burners, heat exchangers, and blowers.
- Boilers: Coverage for leaks, faulty pressure controls, and malfunctioning igniters.
- Heat Pumps: Repairs for compressors, reversing valves, and defrost cycles.
- Controls: Thermostat repairs or replacements might be included.
Top 4 Home Warranty Companies for Central Heating Coverage
Here’s a comparison table showcasing some of the top home warranty companies offering coverage for central heating systems:
|
Companies |
Coverage |
Benefits |
Premiums |
|
|
Up to $3,000 coverage for heating system repairs (may vary by plan). |
|
$29 – $89 |
|
|
|
Up to $1,500 coverage for heating equipment repairs (varies by plan). |
|
$50 – $60 |
|
|
|
Up to $5,000 coverage for heating systems |
|
$45 – $60 |
|
Note: Specific coverage details, pricing, and availability can vary depending on your location and chosen plan.
Additional Tips for Choosing a Home Warranty for Central Heating
- Read the Fine Print: Carefully review the warranty details, coverage limitations, and service call fees before purchasing a plan.
- Consider Your Needs: Choose a plan that offers coverage for your central heating system and other appliances.
- Get Quotes: Compare quotes from multiple home warranty companies before deciding. Look for companies offering coverage in your area.
Conclusion
Understanding your central heating system, identifying potential problems, and taking preventative measures can ensure your home's warm and comfortable winter. For complex issues, always consult a qualified HVAC technician.
related articles
 Discover First American Home Warranty Locations and What You Need to Know About Their Cover.
Discover First American Home Warranty Locations and What You Need to Know About Their Cover.
 Reviews of Home Warranty Companies Show You How to Determine If Your Home Is Covered
Reviews of Home Warranty Companies Show You How to Determine If Your Home Is Covered